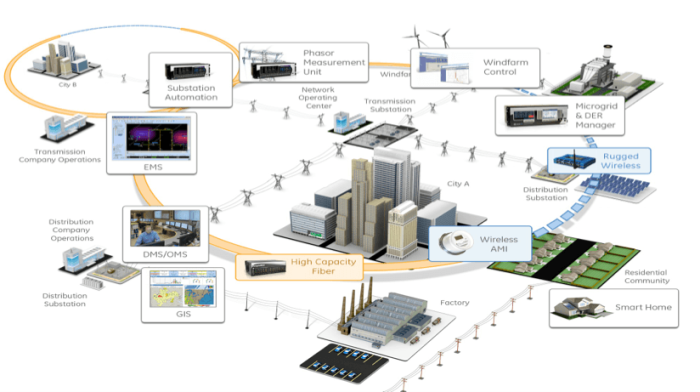
 Smart Grid model (source: the Internet)
Smart Grid model (source: the Internet)
And just recently the emergence of IoT (Internet of Things) may lead mankind to the fourth industrial revolution.
Currently, IoT technology is a growth trend for technological enterprises all over the world. IoT is basically the connectivity of devices to the Internet, in which electric devices communicate to each other and to tablets as well as to the Internet to form a smart system for data exchange and mutual control. IoT has become a technological trend in which increasingly affects the world and has immense application in many futuristic fields, including electricity. The development of IoT can considerably improve efficiency, operation, and implementation of smart grid.
Fundamentally, a smart grid is a network for generation, transmission, distribution and consumption of electricity, which is integrated with applications in fields of IT, communication, data digitalization and modern technology in control, inspection, and supervision. The system enables real-time data and 2-way electricity exchange between suppliers and customers. Smart grid is generally a system for power supply via a merger between the infrastructure of electricity and that of IT. Therefore, the data which are not only successfully collected and processed for operation, system control but also being stored for different purposes based on rules of management and regulation of electricity activities, are very large.
If IT-telecommunication infrastructure is not well-prepared, this will be a big obstacle to the development of smart grid in the future. The emergence of IoT has partly solved such issue when a large amount of high-speed data can be transmitted via Internet protocol. Besides, for electricity consumers, IoT keeps communication between sensors and smart meters continuous, enables automation of devices, such as air conditioners, heating devices, light systems, etc, in an efficient and power-saving way. For substation control system, direct connection to equipment and exchange of data to other managing systems enables detection and handling of anomalous events of the control system, which helps Power Companies achieve the targets: reduction of power losses, power outages without human intervention.
However, the core advantage of IoT in smart grid is the amount of data collected, including real-time data and history data. The data are collected from many different sources of power systems (protection system, control system, smart meters, I/O sets, switching equipment, etc), at substations, plants, houses of customers and other relevant information such as weather, etc. The data will be analyzed, processed and used for load-forecast activity in long-term and medium-term in order to support planning of power supply; limit reduction of electricity due to lack of sources via the mechanism of load transfer during rush hours or emergent cases. Besides, IoT can timely inform electricity consumers at households, manufacturing factories and power companies with electricity quality, consumption, etc.
In order to meet the development of smart grid, Central Power Electronic Measurement Equipment Manufacturing Center (CPCEMEC) has created 19 types of electronic meters that basically meet requirements of electricity metering directly or indirectly, metering in 2 directions, meeting requirements when applying renewable energy into the smart grid. CPCEMEC has studied, cooperated and developed products for supervising power network, including devices for supervising operational parameters of LV network Router 3 phases installed at feeders and branches of distribution network (in cooperation and implementation at Thai Nguyen Power Company) and devices for remote fault alarm of MV power line Remote Alarm (in cooperation with Khanh Hoa Power JSC). CPCEMEC has successfully built software systems for supervising, such as Meter Data Management System (MDMS), Automatic Collection of Data Meter RF SPIDER, System for Supervising Rooftop Solar Power.
With the current development of IoT, CPCEMEC has been studying and testing many different IoT protocols, automated, remote-control devices in order to build a smart grid in IoT trend for electronic devices. Hopefully, IoT system will be fully studied and successfully implemented at EVNCPC in order to support electricity utilities in business and operation.